锚框
目录
目标检测算法通常会在输入图像中采样大量的区域,然后判断这些区域中是否包含我们感兴趣的目标,并调整区域边界从而更准确地预测目标的真实边界框(ground-truth bounding box)。 这些边界框被称为锚框(anchor box)
生成多个锚框
def multibox_prior(data, sizes, ratios):
"""生成以每个像素为中心具有不同形状的锚框"""
in_height, in_width = data.shape[-2:]
device, num_sizes, num_ratios = data.device, len(sizes), len(ratios)
boxes_per_pixel = (num_sizes + num_ratios - 1)
size_tensor = torch.tensor(sizes, device=device)
ratio_tensor = torch.tensor(ratios, device=device)
# 为了将锚点移动到像素的中心,需要设置偏移量。
# 因为一个像素的高为1且宽为1,我们选择偏移我们的中心0.5
offset_h, offset_w = 0.5, 0.5
steps_h = 1.0 / in_height # 在y轴上缩放步长
steps_w = 1.0 / in_width # 在x轴上缩放步长
# 生成锚框的所有中心点
center_h = (torch.arange(in_height, device=device) + offset_h) * steps_h
center_w = (torch.arange(in_width, device=device) + offset_w) * steps_w
shift_y, shift_x = torch.meshgrid(center_h, center_w, indexing='ij')
shift_y, shift_x = shift_y.reshape(-1), shift_x.reshape(-1)
# 生成“boxes_per_pixel”个高和宽,
# 之后用于创建锚框的四角坐标(xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax)
w = torch.cat((size_tensor * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]),
sizes[0] * torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:])))\
* in_height / in_width # 处理矩形输入
h = torch.cat((size_tensor / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[0]),
sizes[0] / torch.sqrt(ratio_tensor[1:])))
# 除以2来获得半高和半宽
anchor_manipulations = torch.stack((-w, -h, w, h)).T.repeat(
in_height * in_width, 1) / 2
# 每个中心点都将有“boxes_per_pixel”个锚框,
# 所以生成含所有锚框中心的网格,重复了“boxes_per_pixel”次
out_grid = torch.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y],
dim=1).repeat_interleave(boxes_per_pixel, dim=0)
output = out_grid + anchor_manipulations
return output.unsqueeze(0)
可以看到[返回的锚框变量Y的形状]是(批量大小,锚框的数量,4)。
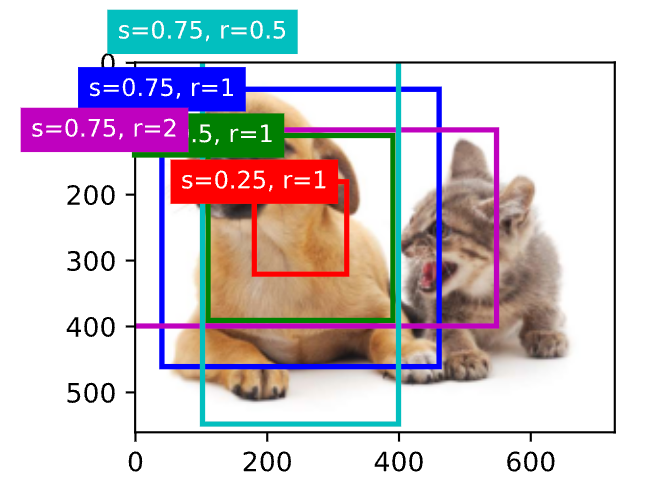
[交并比(IoU)]
事实上,我们可以将任何边界框的像素区域视为一组像素。通
过这种方式,我们可以通过其像素集的杰卡德系数来测量两个边界框的相似性。
对于两个边界框,它们的杰卡德系数通常称为交并比(intersection over union,IoU),即两个边界框相交面积与相并面积之比。
交并比的取值范围在0和1之间:0表示两个边界框无重合像素,1表示两个边界框完全重合。